What is loadbalancing?
Loadbalancing stands for the distribution of workload among multiple servers. The Loadbalancer is responsible for distributing the workload, and monitoring the status and state of load on all existing slaves. By setting up a loadbalance situation you can distribute your services across multiple servers, so it is for example possible to divide a Web server into multiple servers that serve the same site(s) and pages. This principle applies to tasks such as Apache, Lighttpd, FTP, etc. The handling of the requested services in a load balance situation does not differ from a normal situation. The data traffic between the Loadbalancer, Slaves and optional extra servers is always done locally, you will not pay any extra traffic.
The use of a loadbalancer is practical when your website(s) have become too busy to load from one server.
Configuration
Base:
2x Slaves
1x Loadbalancer
1x 1U 100Mbit switch.
Optional:
Practically, there is no limit to the amount of slaves of a loadbalancer.
Database server(s)
Backup Loadbalancer(s)
1x 1U 1000Mbit or 10.000 Mbit switch.
Schematic overview
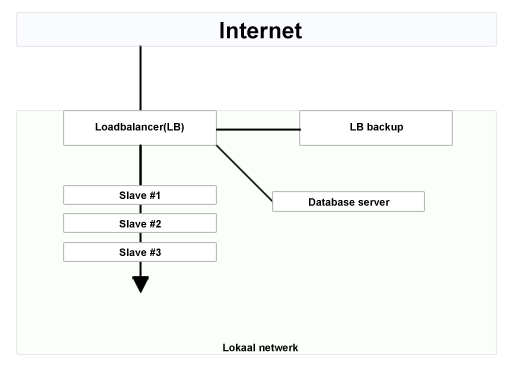

Rates
Since the setup of a Load Balance situation is always custom made, it is not possible to specify a default price here. You can contact us explaining your situation, and we will come up with a specific plan for your situation and send you a cost estimate.
Terminology
Loadbalancer: A server that has the function to distribute one or more tasks to designated slaves.
Slave: A (web)server that has the task to serve one or more tasks to the loadbalancer
Workload: A description for the amount of usage (stress) on the processor, memory, disk I/O of a (web)server
Apache: The default webserver for Linux. Apache makes it possible to offer your websites and files to visitors.
Lighttpd: An alternative to Apache. Lighttpd is best described as a lighter version of Apache, best suited to serve static files
FTP: File Transfer Protocol, a simplistic method of transferring files (data) between 2 computers.